AI Strategy in an Uncertain World: What Business Leaders Need to Know This Week
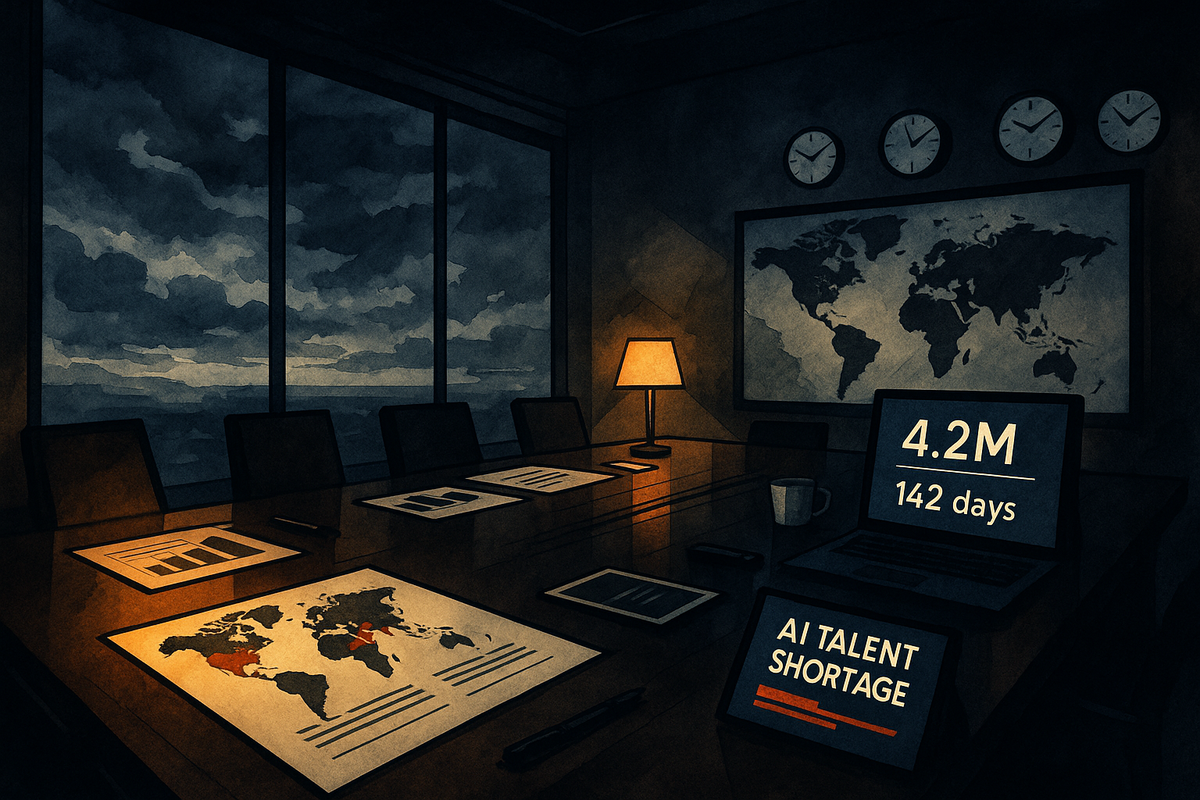
The AI talent shortage reaches crisis levels with 4.2 million unfilled positions globally. Strategic intelligence on corporate concentration, policy developments, and competitive positioning indicators.

Strategic Intelligence Brief - Monday, June 23, 2025
This Week's Critical Developments
- AI talent shortage reaches 4.2M unfilled positions - creating binary strategic choices for organizations
- Corporate talent concentration accelerates - Meta's 3,600 layoffs signal "wartime" talent strategies
- Policy landscape crystallizes - H-1B enforcement and Congressional AI moratorium create new constraints
The global business environment feels genuinely uncertain right now. Geopolitical tensions shift daily, economic indicators send mixed signals, and policy frameworks change faster than most organizations can adapt. In this landscape of constant flux, executive teams need reliable intelligence to make sound strategic decisions about their AI investments and talent strategies.
While we can't predict every policy reversal or market shock, we can analyze what the data tells us about AI talent markets, corporate positioning, and regulatory developments. This intelligence brief examines three critical developments reshaping AI strategy this week: a talent shortage reaching crisis proportions, accelerating corporate bifurcation in talent concentration, and policy changes creating new constraints and opportunities.
The promise here is strategic guidance based on solid intelligence, not speculation—because in uncertain times, decision quality depends on data quality.
What We Know Today
The Talent Crisis Reaches Breaking Point
The numbers are stark and getting worse. There are currently 4.2 million unfilled AI positions globally with only 320,000 qualified developers available to fill them. This represents a hiring gap of approximately 50%, meaning only half of required AI roles can be filled based on current supply.
The operational impact is measurable and severe. The average time to fill an AI position has risen to 142 days, while companies face an average annual cost of $2.8 million each due to delays in AI initiatives caused by talent shortages. Perhaps more concerning, 87% of organizations report struggling to hire AI talent, with AI developer compensation up 32% year-over-year as companies bid aggressively for scarce resources.
This isn't just a hiring challenge—it's a fundamental constraint on AI strategy execution that's forcing difficult organizational choices.
The skills shortage in specialized computing infrastructure has reached 61% of open positions, up from 53% just last year. Organizations need not only data scientists and AI engineers, but professionals capable of designing, deploying, and optimizing the specialized hardware and cloud infrastructure required for modern AI workloads. The rapid adoption of generative AI has intensified demand for infrastructure experts who can support large-scale, resource-intensive AI models.
Most troubling for long-term strategy, the new graduate pipeline is broken. Hiring of new graduates by major tech companies has fallen 50% since 2019, with new grads now accounting for just 7% of all hires at Big Tech firms. Universities are producing 40% fewer AI-ready graduates than industry demand requires, while the unemployment rate for recent college graduates rose to 5.8% in March 2025—not because there aren't jobs, but because there's a fundamental mismatch between academic preparation and industry requirements. September academic year data will reveal whether universities can meaningfully address this 40% pipeline shortage.
Corporate Strategy Bifurcation Accelerates
The talent shortage is creating a decisive moment for corporate strategy. Organizations are being forced into stark strategic choices, creating a clear bifurcation between aggressive talent concentrators and status quo maintainers.
Meta exemplifies the concentration strategy with its recent 3,600 strategic layoffs targeting 5% of its workforce—specifically "low performers" as part of what executives term an "intense year" focused on AI competitiveness. This isn't traditional cost-cutting; it's systematic talent reallocation toward AI capabilities while eliminating roles that don't contribute to strategic priorities.
The market split is becoming pronounced. Amazon, Google, and Microsoft are maintaining 3,000+ AI engineering roles despite broader workforce reductions, reallocating resources internally to bolster AI, cloud, and machine learning teams. Meanwhile, companies taking a "wait and see" approach find themselves increasingly disadvantaged as the shortage accelerates.
The retention battlefield reveals which strategies work. Anthropic maintains an 80% retention rate compared to OpenAI's 67%—a significant gap that demonstrates culture-over-compensation effectiveness. Anthropic's success stems from emphasizing autonomy, intellectual freedom, and mission alignment around AI safety, factors that prove more compelling to top talent than pure compensation competition.
This pattern extends beyond headline companies. Engineers at OpenAI are 8 times more likely to leave for Anthropic than vice versa, while at DeepMind that ratio reaches 11:1 in Anthropic's favor. The flow of talent consistently moves from established giants to organizations offering greater autonomy and clearer mission alignment. July Q2 earnings will separate companies with genuine AI talent ROI from those still in the investment phase.
These developments signal a fundamental shift: the AI talent market is consolidating around companies that combine strategic focus with cultural differentiation.
Policy Landscape Creates New Constraints and Opportunities
Regulatory and immigration changes are reshaping the competitive landscape in ways that favor prepared organizations over reactive ones.
The H-1B modernization rule, effective January 17, 2025, introduces enhanced enforcement mechanisms including mandatory site visits, penalty authority, and stricter compliance requirements. While the rule provides some flexibility in specialty occupation definitions and extends cap-gap protection for F-1 students, the enforcement escalation creates meaningful compliance costs for unprepared organizations. H-1B enforcement actions, now 6 months post-implementation, should surface in July data showing which companies face significant compliance costs versus those who prepared effectively.
Congressional action on AI regulation reached a critical juncture with the 10-year federal moratorium on state and local AI regulation clearing a Senate procedural hurdle in June 2025. The House passed this provision by a narrow 215-214 vote, and despite Republican party splits on states' rights grounds, the measure appears likely to advance. This creates a regulatory landscape trending toward incumbent advantage, as established players benefit from reduced regulatory fragmentation while smaller competitors lose potential state-level protection or support.
Immigration enforcement intensification creates both constraints and arbitrage opportunities. For companies with existing offshore operations in Canada, Singapore, or the UK, these policy changes create incentives to deepen AI investments as regulatory hedges. August policy arbitrage data will show which companies successfully executed international talent strategies while others remained domestically constrained.
Strategic Implications
The convergence of talent shortages, corporate concentration strategies, and policy changes creates three critical implications for strategic planning.
The Talent Strategy Ultimatum
The data presents a binary choice: aggressive talent concentration or competitive decline. With 4.2 million unfilled positions and only 320,000 qualified developers, companies must decide whether to compete aggressively for talent or accept strategic disadvantage.
Meta's "wartime versus peacetime" strategic positioning illustrates this dynamic. While traditional HR approaches focus on broad workforce management, Meta's targeted performance management enables systematic talent reallocation toward AI capabilities. Companies implementing clear performance standards can redeploy resources from lower-impact roles to critical AI functions—but this requires decisive leadership and systematic execution.
The mathematics are stark: first-mover advantages in talent acquisition compound rapidly in constrained markets. The 142-day average hiring timeline means that decisive action in Q2 delivers Q4 competitive positioning, while indecision creates cumulative disadvantage. Organizations that secure AI talent now avoid competing in even tighter markets later.
The cost of indecision escalates measurably. Beyond the $2.8 million annual cost per company from project delays, organizations face opportunity costs as competitors advance AI capabilities while they struggle with unfilled positions. Summer hiring patterns may invert traditional seasonality due to critical shortage levels, creating opportunities for companies willing to act counter-cyclically.
Performance management emerges as a strategic weapon rather than an administrative function. Organizations like Meta use systematic performance evaluation to identify talent for reallocation toward AI initiatives, essentially creating internal talent markets that optimize resource allocation without external hiring constraints.
Geographic and Policy Hedging Imperatives
Policy constraints are creating new competitive advantages for strategically positioned organizations. Smart geographic positioning offers sustainable competitive advantages as talent becomes increasingly mobile and policy enforcement tightens.
For companies with existing offshore operations, current conditions favor deepening AI investments in Canada, Singapore, and the UK as hedges against H-1B constraints. These markets offer established talent pools, favorable immigration policies for skilled workers, and regulatory environments supportive of AI development.
The Congressional AI moratorium, if passed, creates regulatory arbitrage between federal and state-level innovation policies. Companies can optimize geographic footprint based on regulatory clarity rather than hoping for favorable state-level policies. This trend toward incumbent advantage rewards organizations with resources to navigate federal compliance over smaller competitors dependent on state-level support.
Market Timing Intelligence and Forward Indicators
Current shortage conditions will likely worsen before improving, creating specific windows for strategic action by prepared organizations.
The university pipeline producing 40% fewer AI-ready graduates than industry demand means shortage conditions persist through at least 2026. Organizations cannot rely on increased graduation rates to solve talent constraints. Corporate-university partnership announcements expected before fall semester represent companies competing for exclusive pipeline access as traditional recruitment proves inadequate.
Economic uncertainty creates a paradoxical opportunity: hiring windows for cash-prepared companies. While competitors defer AI talent investments due to broader economic concerns, organizations with strong balance sheets can acquire talent at relatively lower competition levels.
The key insight: Silicon Valley wage dynamics show recent declines likely to reverse sharply in Q3-Q4 2025 as talent shortage effects compound. Companies expanding AI teams now benefit from temporarily compressed compensation expectations before market conditions tighten further.
Strategic Framework for Leaders
Talent Strategy Priorities in Constrained Markets
Success in 142-day average hiring environments requires systematic retention investment over acquisition strategies. The Anthropic model offers actionable insights: organizations like Anthropic demonstrate that culture, autonomy, and mission alignment create sustainable talent advantages that pure compensation cannot match.
The cultural differentiation approach becomes increasingly valuable as compensation inflation makes bidding wars unsustainable for most organizations. Emphasizing intellectual freedom, flexible work arrangements, and clear mission alignment around technological impact attracts and retains talent more effectively than salary competition alone.
Training programs become critical differentiators when universities produce 40% fewer qualified graduates than industry needs. Organizations must build internal capability development rather than relying on external talent supply.
Risk Management and Scenario Planning
Policy hedge positioning requires geographic diversification strategies for organizations facing regulatory uncertainty. Companies should evaluate international expansion options before policy constraints tighten further, particularly in jurisdictions with favorable immigration policies and established AI talent pools.
The strategic imperative: supply chain and workforce resilience planning must account for talent shortage effects on project timelines and capability development. Organizations need contingency plans for 142-day hiring cycles and systematic approaches to capability gaps that don't depend solely on external recruitment.
Competitive intelligence on talent concentration strategies becomes strategically critical. Organizations need systematic monitoring of competitor hiring patterns, retention strategies, and geographic expansion to anticipate competitive moves and identify talent acquisition opportunities.
Bottom Line Strategic Decision Point
The AI talent crisis forces a binary choice: concentrate talent aggressively or accept competitive disadvantage. Companies that act decisively on current intelligence—whether through geographic hedging, cultural differentiation, or systematic performance management—position themselves advantageously regardless of future market developments. Those waiting for certainty will find themselves reacting to competitors who acted on available data.
Strategic Intelligence Indicators: 90-Day Forward Monitoring
Strategic leaders should monitor specific developments over the next 90 days that will clarify market direction and competitive positioning:
July Q2 Earnings Analysis: Corporate earnings will reveal which companies achieve measurable ROI from AI talent concentration strategies versus those still in investment phases. This data will drive copycat strategies and competitive positioning for Q3-Q4 planning.
August Congressional Action: Senate action on the 10-year state AI regulation moratorium will determine geographic strategic positioning and regulatory arbitrage opportunities. Either passage or failure creates immediate implications for AI investment geography.
September Academic Capacity Data: New academic year enrollment and graduation projections will clarify whether university AI programs can meaningfully address the 40% pipeline shortage, influencing corporate training investment and partnership strategies.
Wild Card Monitoring: Watch for talent-focused acquisition strategies as companies buy smaller firms specifically for engineering teams rather than technology. Industry consolidation may accelerate as talent shortage forces strategic combinations focused on human capital rather than intellectual property.
Continued Intelligence Commitment
These developments illustrate why systematic intelligence gathering matters more than prediction in uncertain environments. While we cannot forecast every policy shift or market disruption, we can analyze emerging patterns and provide frameworks for strategic decision-making under uncertainty.
The AI talent crisis represents a fundamental market structure change, not a temporary shortage. Organizations that adapt strategies now based on current intelligence position themselves advantageously regardless of specific future developments. Those that wait for certainty will find themselves reacting to competitors who acted on available data.
This intelligence brief represents our commitment to monitoring developments and updating analysis based on emerging data rather than speculation. Next week's Research Tuesday deep-dive will examine implementation patterns from organizations successfully navigating talent constraints, providing tactical frameworks for strategic execution.
For strategic leaders facing AI talent concentration decisions, the choice is becoming binary: act on current intelligence or accept competitive disadvantage. The data supports action for prepared organizations while cautioning against delay.
Strategic intelligence continues. Market conditions require systematic analysis over reactive speculation.